Describe What Happens When a Muscle Contracts.
It can happen when you hold or pick up something. Describe what is involved in muscle contraction.
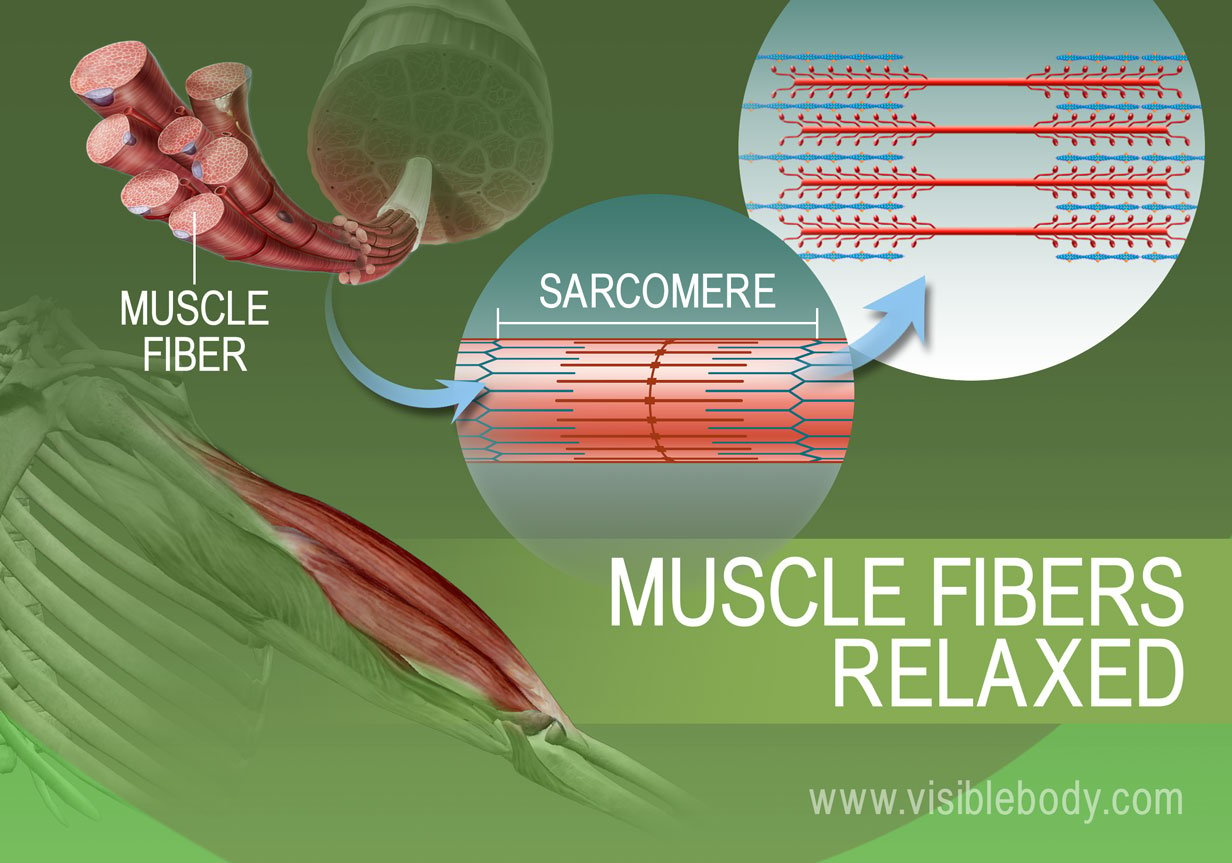
Muscle Contractions Learn Muscular Anatomy
Then the myosin heads bind to actin and cause the actin filaments to slide.

. Muscle contraction begins when the nervous system generates a signal. Lightning is an example of what phenomenon. Health 22062019 1500 Teddybearnerd.
This makes the sarcomeres shorter and thicker contracting the muscle. The myofibrils shorten 3 too as does the whole muscle cell. This stimulates the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium into the muscle cell.
Describe how you would communicate with patients that chose the physician assisted suicide option. The head group then bends causing the think filament to be pulled along and so overlap more with the thick filaments. Describe the sliding-filament mechanism of muscle contraction.
Describe what happens when a muscle contracts. Describe what happens to the size of each band A band H zone zone of overlap I band within the sarcomere during a contraction increase decrease or no change. A signal is sent from the brain or.
Calcium floods into the muscle cell binding with troponin allowing actin and myosin to bind. Acetylcholine binds with receptors on. The signal an impulse called an action potential travels through a type of nerve cell called a motor neuron.
The actin and myosin cross bridges bind and. 1 The sequence of events leading to contraction is initiated somewhere in the central nervous system either as voluntary activity from the brain or as reflex activity from the spinal cord. Define and describe a synapse and identify the neurotransmitter that is present in the neuromuscular junction NMJ.
When the muscle contracts the joint between the two attachments acts as a lever and causes motion that moves that part of the body. A Muscle Contraction Is Triggered When an Action Potential Travels Along the Nerves to the Muscles. A muscle contraction consists of a series of repeated events.
What are the steps in muscle contraction. The motor nerve stimulates an action potential impulse to pass down a neuron to the neuromuscular junction. In other words for a muscle cell to contract the sarcomere must shorten.
2 A motor neuron in the ventral horn of the spinal cord is activated and an action potential passes outward in a ventral root of the spinal. This results in shortening of the sarcomere. When a sarcomere shortens some regions shorten whereas others stay the same length.
If you prefer a hands on learning experience you might be interested in this giant sarcomere model on Amazon. For thin filaments to continue to slide past thick filaments during muscle contraction myosin heads must pull the actin at the binding sites detach re-cock attach to more binding sites pull detach re-cock etc. During muscle contraction the actin filament is pulled along myosin toward the centre of the sarcomere until the actin and myosin filaments are completely overlapped.
When a muscle contracts the actin is pulled along myosin toward the center of the sarcomere until the actin and myosin filaments are completely overlapped. First calcium triggers a change in the shape of troponin and reveals the myosin-binding sites of actin beneath tropomyosin. During a muscle contraction every sarcomere will shorten 1 bringing the Z-lines closer together 2.
A little muscle contraction fun. Muscle Contraction Steps in Detail. Other questions on the subject.
An action potential in a motor neuron causes acetylcholine to release in the synaptic cleft. This repeated movement is. In order to contract a muscle the first thing that needs to occur is that there must be an influx of calcium ions.
When the CNS sends a signal the thick and thin myosin filaments form a crossbridge pattern by sliding past each other. This is the power stroke. The unstimulated state of the muscle cell called the resting potential is created by the presence of large negatively charged proteins and nucleic.
Describe what happens when a muscle contracts. Repetition of these events causes a muscle to contract. A release of a large amount of energy an.
The following steps are involved in muscle contraction. In the resting state the globular myosin heads are not bound to the actin molecules preventing this bonding from occurring are two molecules called troponin and tropomyosin. Myosin head groups attach to the surrounding actin filaments forming a cross-bridge.
Cardiac Muscle Contraction The sarcolemma plasma membrane of an unstimulated muscle cell is polarizedthat is the inside of the sarcolemma is negatively charged with respect to the outside. 1 Show answers Another question on Physics. If the textbook weighs 196 newtons on venuswhat is the strength of gravity on venus.
What happens after. The primary mode of action for muscle is by contraction. Yet the myofilaments the thin and thick filaments do not get shorter 4.
So lets do a quick review of muscle contraction physiology. ATP and Muscle Contraction. These calcium ions cause the troponin that fixes the position of the tropomyosin to.
Muscle contraction is the tightening shortening or lengthening of muscles when you do some activity. Grendeldekt and 2 more users found this answer helpful.

Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And Physiology I

Muscular Contraction 6 3 4 Aqa A Level Biology Revision Notes 2017 Save My Exams


Comments
Post a Comment